bio energy

It is renewable energy available from living sources, and it is considered a form of solar energy because it stores sunlight in organic matter in the form of chemical energy. Organic materials are the remains of living organisms from plants and animals and their waste in the natural environment in addition to food residues
We can benefit from organic matter by converting it into biofuel or biogas Biofuels are extracted from palm oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, corn, sugar cane and rapeseed. Another substance that has received great attention now is algae.
Characteristics of Bioenergy Routes A bioenergy chain or route consists of a series of conversion steps by which a raw biomass feedstock is transformed into a final energy product (heat, electricity or transport biofuel
By which biomass undergoes chemical degradation induced by high temperature. These thermochemical routes are combustion, gasification, pyrolysis and torrefaction.
Is used to produce liquid fuels (biodiesel or vegetable oil) from oil crops (rapeseed, soybean, jatropha, etc.) by oil extraction possibly followed by a transesterification process. Biological routes Use living micro-organisms (enzymes, bacteria) to degrade the feedstock and produce liquid and gaseous fuels.
fermentation: from sugar (sugar cane, sugar beat, etc.), starch (corn/maize, wheat, etc.) lignocelluloses (grass, wood, etc.) feedstock. Anaerobic digestion (mostly from wet biomass). Bio-photochemical routes (hydrogen producing using algae) which require the action of sunlight.
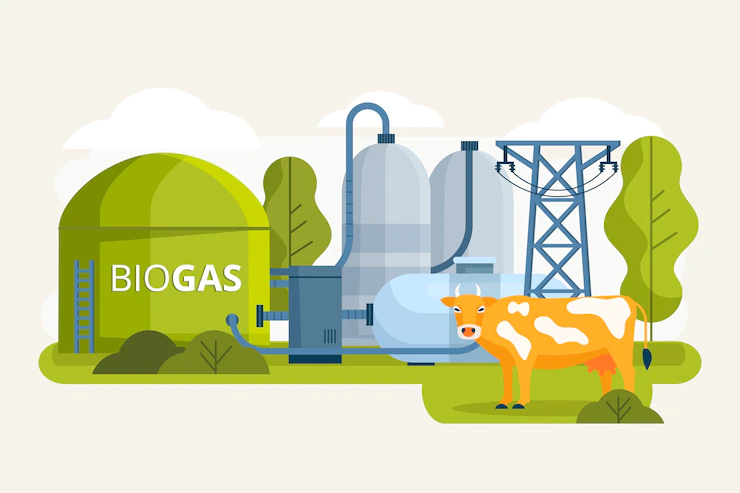
Biogas is produced naturally from the decomposition of waste, and this occurs when the biological material such as food waste or animal waste is present in an oxygen less environment, and this results in a mixture of gases that constitutes methane, the largest part of it, and this process takes place in the absence of air, it is called anaerobic digestion
We can produce biogas automatically by creating a reaction, and the resulting gas is used in electricity generation, in heating, in cooking, or as fuel for vehicles. This method of producing electricity is considered one of the renewable energy methods, where we can obtain the biological material permanently
Anaerobic digestion is a group of biological processes catalyzed by micro-bacteria. These bacteria break down degradable materials in an oxygen less atmosphere, resulting in biogas that can be used to generate electrical energy or convert it into fuel for biogas-powered machinery.
Anaerobic digestion is a natural process of converting waste products into energy. Animal manure, food residues, and sewage water are examples of organic materials that can produce biogas through anaerobic digestion. The proportion of methane in it is between 70% to 75%, so biogas is flammable. And it can be used as a power source
There are many anaerobic digestion systems currently available, and we will mention some of the methods used in the analysis of wastewater, industrial waste and animal manure in order to reduce methane emissions and harmful and disease-causing odors in addition to the production of biogas
A small lake containing the biological material is covered with a tightly closed cover with pipes to extract the resulting methane gas and direct it to the combustion device. Some systems use a digester and one common tank
This digester is a rectangular tank with a sealed shape that does not use a mixer and is mainly used to digest the organic products of dairy farms The manure is collected and entered into the tank, where it is analyzed as it passes through the tank, and the tank is covered with a heavy cover
This system can be modified to produce energy in any climate unlike the lake system of anaerobic digestion in addition to the fact that the digested solid products can be separated and sold as a new product
The complete mixing system is an advanced technology to achieve better quality and greater quantity of biogas This system produces biogas from different types of organic waste, so that solid waste forms from 3% to 10%. To improve the energy production process, the waste is heated and mixed well to ensure a high level of bacteria spread, and a cover is placed to prevent gas leakage
Temperature within the digester is critical with maximum conversion occurring at approximately 95F in conventional digesters For each 20F decrease in temperature, gas production falls by approximately 50%.
Waste is collected in silos similar to grain silos built of cement or iron and closed with a steel cover Dry digestion works with solid waste, which constitutes 20% to 42% of the total waste, which allows in this way to combine fertilizers containing a high percentage of solid materials and crop residues with liquid fertilizer